Langford, British Columbia
Langford | |
|---|---|
| City of Langford | |
 Goldstream Village, centre of Langford | |
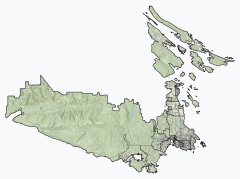
Location of Langford within the Capital Regional District | |
| Coordinates: 48°27′2″N 123°30′21″W / 48.45056°N 123.50583°W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | British Columbia |
| Regional district | Capital |
| Founded | 1851 |
| Incorporated | December 8, 1992 |
| Government | |
| • Governing body | Langford City Council |
| • Mayor | Scott Peter Goodmanson |
| • Councillors | Colby Harder, Mary Wagner, Keith Yacucha, Kimberley Guiry, Mark Morley, Lillian Szpak |
| Area | |
| • Land | 41.43 km2 (16.00 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 76 m (249 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 46,584 |
| • Density | 1,124.4/km2 (2,912/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Langfordite, Langfordian |
| Time zone | UTC−8 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7 (PDT) |
| Postal code | V9B, V9C |
| Area code(s) | 250, 778, 236, 672 |
| Highways | |
| Website | langford |
Langford is a city on southern Vancouver Island in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Langford is one of the 13 component municipalities of Greater Victoria and is within the Capital Regional District. Langford was incorporated in 1992 and has a population of over 40,000 people, the largest municipality in the Western Communities, and third-largest in the Capital Regional District after Saanich and Victoria.
Its motto is "Golden in setting, determined in Spirit," containing a reference to the natural beauty of the City of Langford, specifically Goldstream Provincial Park, and a comment on the community's drive to enhance Langford's special character and future.[2]
History
[edit]Langford's history of European settlement dates back to 1851, when Captain Edward Langford[3] established one of the four Hudson's Bay Company farms in the Victoria area. He arrived with his family in 1851 as the first English family to emigrate to the Colony of Vancouver Island. He was the manager of the Esquimalt farm owned by the Puget Sound Agricultural Company, a subsidiary of the Hudson's Bay Company. He returned to England in 1861.[4]: 149
In the early 1860s, the region of Langford experienced a short-lived gold rush in what is now Goldstream Provincial Park.[5][6] The area was once a favourite recreation destination for thousands of Victorians in the late 1800s: day-trippers travelled via railway to the popular country resort Goldstream House Hotel;[7] hunters built their lodges on the shores of the lakes near the mountains; and a summer colony of the well-to-do city folk relaxed and socialized at Langford Lake.[8]
Langford was incorporated on December 8, 1992.[9], and became a city in 2003.
In the 2010s, the city has become the fastest-growing on Vancouver Island, with big retail stores and new residential developments.
Geography
[edit]
Langford is the urban core of the five suburban municipalities comprising the region of West Shore for a combined population of about 75,000. Its municipal neighbours are Colwood to the southeast, Highlands to the north, Metchosin to the southwest, and View Royal to the northeast.
Notable physical features of Langford include the three prominent lakes (Langford Lake, Glen Lake and Florence Lake) stocked with Trout, and the Humpback Reservoir, several peaks such as Mount Finlayson and Mount Wells, and the notable Goldstream Provincial Park. The Malahat drive, part of the Trans-Canada Highway, begins in Langford, and the Galloping Goose Regional Trail and the Island Rail Corridor cross the city.
Langford enjoys a temperate climate with mild temperatures and distinct dry and rainy seasons.[10] Most built-up areas in Langford are on basalt bedrock, while lower-lying regions of the Langford Plain from Langford Lake to Royal Bay are glacial till, and Happy Valley and Goldstream River valley are on deep sand of the Colwood Delta.[11]
Old growth forestlands were once abundant in Langford but urban sprawl threatens natural habitat including coastal Douglas fir, western red cedar, arbutus trees and Garry oak ecosystems. The last remaining pockets of arbutus groves and Garry oak meadows are unique to southern Vancouver Island and only about five percent of the ecosystems remain in their natural state. The unique Mediterranean characteristics of the island's climate support the Garry oak ecosystem in the few remaining undeveloped areas of Langford, and are under threat due to rapid growth, high-density subdivisions, and urbanization.[12]
Neighbourhoods
[edit]- (South) Langford Proper/ Goldstream Village/ Langford Lake[13]
- Humpback/ Goldstream Meadows
- Westhills[14] [15]
- Glen Lake
- Luxton/ Happy Valley[16]
- Triangle Mountain/ Walfred
- Olympic View/ Latoria
- Mill Hill/ Atkins
- North Langford/ Millstream
- Thetis Heights[17]
- Florence Lake surrounded by temporate rain forest is home to the Hidden Valley Mobile home park
- Bear Mountain[18]
Demographics
[edit]In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Langford had a population of 46,584 living in 19,050 of its 19,968 total private dwellings, a change of 31.8% from its 2016 population of 35,342. With a land area of 41.43 km2 (16.00 sq mi), it had a population density of 1,124.4/km2 (2,912.2/sq mi) in 2021.[1]
Langford is the fastest growing community in British Columbia and the third fastest growing city in Canada in the 2021 census, attracting new residents from all over Greater Victoria, the Lower Mainland, Ontario, and Alberta due to new housing developments, a strong real estate market and affordability, a desirable temperate climate with warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters, ample amenities as the commercial centre of West Shore, and year-long recreational activities.[19][20]
The median household income in 2015 for Langford was $80,331, which is almost 15% higher than the British Columbia provincial average of $69,995.[21]
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Population counts are not adjusted for boundary changes. Source: Statistics Canada[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethnicity
[edit]| Panethnic group |
2021[1] | 2016[21] | 2011[22] | 2006[23] | 2001[24] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | Pop. | % | |
| European[a] | 35,845 | 77.6% | 29,230 | 83.71% | 25,220 | 87.1% | 20,010 | 89.75% | 17,160 | 91.94% |
| Indigenous | 2,685 | 5.81% | 2,090 | 5.99% | 1,490 | 5.15% | 940 | 4.22% | 665 | 3.56% |
| Southeast Asian[b] | 1,935 | 4.19% | 825 | 2.36% | 410 | 1.42% | 320 | 1.44% | 55 | 0.29% |
| South Asian | 1,880 | 4.07% | 910 | 2.61% | 690 | 2.38% | 490 | 2.2% | 270 | 1.45% |
| East Asian[c] | 1,720 | 3.72% | 1,000 | 2.86% | 655 | 2.26% | 235 | 1.05% | 225 | 1.21% |
| African | 725 | 1.57% | 250 | 0.72% | 180 | 0.62% | 100 | 0.45% | 120 | 0.64% |
| Latin American | 640 | 1.39% | 375 | 1.07% | 155 | 0.54% | 85 | 0.38% | 50 | 0.27% |
| Middle Eastern[d] | 390 | 0.84% | 120 | 0.34% | 80 | 0.28% | 20 | 0.09% | 0 | 0% |
| Other[e] | 370 | 0.8% | 120 | 0.34% | 55 | 0.19% | 105 | 0.47% | 100 | 0.54% |
| Total responses | 46,190 | 99.15% | 34,920 | 98.81% | 28,955 | 99.07% | 22,295 | 99.27% | 18,665 | 99.07% |
| Total population | 46,584 | 100% | 35,342 | 100% | 29,228 | 100% | 22,459 | 100% | 18,840 | 100% |
- Note: Totals greater than 100% due to multiple origin responses.
Religion
[edit]According to the 2021 census, religious groups in Langford included:[1]
- Irreligion (28,590 persons or 61.9%)
- Christianity (14,450 persons or 31.3%)
- Islam (685 persons or 1.5%)
- Hinduism (625 persons or 1.4%)
- Sikhism (600 persons or 1.3%)
- Buddhism (370 persons or 0.8%)
- Judaism (220 persons or 0.5%)
- Indigenous Spirituality (65 persons or 0.1%)
Amenities
[edit]Activities in Langford include shopping at the many retail stores on Goldstream Ave, Millstream Village[25] and Westshore Town Centre[26] (formerly Canwest Mall) with its 55 stores and services including major department, grocery, and retail chain stores as well as a seven-screen Cineplex[27] movie theatre.[28][29]
Langford's city parks include City Centre Park,[30] with a family-friendly entertainment zone including a Family Fun Park,[31] and Veterans Memorial Park[32] located in the heart of downtown, and at the centre a cenotaph commemorating the men and women of the Canadian Forces who have given their lives in the line of duty and where Langford holds its yearly Remembrance Day ceremony on Nov 11.
Community events include parades, a seasonal farmer's market,[33] the Summer Festival, and Luxton Fair in September.[34] Rugby Canada[35] has its headquarters in Langford practising at Starlight Stadium. A new $30 million YMCA/YWCA Aquatic Centre[36] opened in May 2016, acclaimed by the mayor to be the "biggest project in the history of Langford", and features multiple pools, recreation facilities and a new library.[37]
Langford is home to golf courses including Bear Mountain Resort[38] on Skirt Mountain. The large community resort offers a system of mountain bike trails as the training centre for the Canadian National Mountain Bike Team[39] and is planning the development of clay tennis courts for the national team and a professional disc golf course.[40]
There are many lakes in the area for fishing, swimming and non-motorized boating including Langford, Glen and Florence Lake. Langford is known for the many nature parks and a network of trails popular with hikers and walkers alike including Mill Hill Park, Mount Wells, Thetis Lake Regional Park and the challenging high-elevation Mount Finlayson. Cyclists enjoy the picturesque multi-use Galloping Goose Trail, formerly a Canadian National railway line, that moves through urban and rural parts of Langford and is used as a commuter trail to downtown Victoria, approximately 45 minutes away by bicycle. Goldstream Provincial Park is a large 477 ha (1,180 acres) nature reserve home to old-growth trees, waterfalls, estuaries and a visitor centre and Nature House[41] offering many visitor activities such as camping, picnicking, hiking, and wildlife watching like eagle viewing during the annual salmon run.[5][42]
Services
[edit]
Langford has three fire stations [43] with a mix of 60 volunteer and career members.led by Chief Chris Aubrey ref name="City of Langford - Fire Department"/>
The region is policed by the West Shore detachment[44] of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police. Additionally, Langford is also home to the central BC Ambulance 911 call centre, located at 2764 Leigh Rd, which provides 911 dispatch services to Vancouver Island and the surrounding islands.[45][46][47][48]
Education
[edit]Langford is a part of the School District 62 Sooke with approximately 12,900 students in 2023.[49] The school district serves the communities of Sooke, Port Renfrew, Metchosin, Colwood, Highlands, and Langford. Ten of the 25 schools are in Langford including one middle school and one high school. In 2015, two new state-of-the-art high schools[50] were built to a LEED Gold standard to replace the 65-year-old Belmont high school: lake-front Belmont Secondary School (the largest on Vancouver Island) in Langford with a capacity of 1,200-students, and the ocean-side Royal Bay Secondary School in Colwood with 800 students.[50] Both high schools are already overcapacity due to rapidly expanding region. There is also the Westshore Centre for Learning and Training, and the Lighthouse Christian Academy[51] which serves Kindergarten to Grade 12.
Notable people
[edit]- Tyson Barrie, NHL player
- Ryder Hesjedal, Canadian Olympian and professional racing cyclist
- John Horgan, Former Premier of British Columbia[52]
- Moka Only, musician
- Bob Rock, musician
- Jennifer Tilly, actor
- Meg Tilly, actor
Notes
[edit]- ^ Statistic includes all persons that did not make up part of a visible minority or an indigenous identity.
- ^ Statistic includes total responses of "Filipino" and "Southeast Asian" under visible minority section on census.
- ^ Statistic includes total responses of "Chinese", "Korean", and "Japanese" under visible minority section on census.
- ^ Statistic includes total responses of "West Asian" and "Arab" under visible minority section on census.
- ^ Statistic includes total responses of "Visible minority, n.i.e." and "Multiple visible minorities" under visible minority section on census.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f "Langford, City [Census subdivision], British Columbia and Capital, Regional district [Census division], British Columbia". Statistics Canada. February 8, 2023. Retrieved March 20, 2023.
- ^ "City of Langford – Coat of Arms". Cityoflangford.ca. Archived from the original on 2016-10-26. Retrieved 2015-05-17.
- ^ John Beadler. "Biography – LANGFORD, EDWARD EDWARDS – Volume XII (1891–1900) – Dictionary of Canadian Biography". Biographi.ca.
- ^ Akrigg, G.P.V.; Akrigg, Helen B. (1986), British Columbia Place Names (3rd, 1997 ed.), Vancouver: UBC Press, ISBN 0-7748-0636-2
- ^ a b "Goldstream Provincial Park". Env.gov.bc.ca.
- ^ "The gold rush at Goldstream, BC". Bcgoldrushpress.com. Archived from the original on 2016-04-22. Retrieved 2015-05-17.
- ^ "Dunsmuir's Inaugural Train Trip – Goldstream Hotel – Old Langford excerpt". Maureenduffus.com.
- ^ "Old Langford – An Illustrated History – Maureen Duffus". Maureenduffus.com.
- ^ "City of Langford – Home". Cityoflangford.ca. Archived from the original on 2022-05-26. Retrieved 2015-05-17.
- ^ "Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000 Station Data". Climate.weather.gc.ca. 31 October 2011.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2015-05-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Protecting our natives – Canadian Geographic Magazine: In-depth". Canadiangeographic.ca.
- ^ "Downtown". City of Langford. Retrieved 2023-12-11.
- ^ "Westhills BC – New Home Community in Victoria's Westshore". Westhillsbc.com.
- ^ "Westhills". City of Langford. Retrieved 2023-12-11.
- ^ "City of Langford – Happy Valley". Cityoflangford.ca.
- ^ "City of Langford – Thetis Heights". Cityoflangford.ca.
- ^ "Bear Mountain". City of Langford. Retrieved 2023-12-11.
- ^ "Langford, B.C. ranked 3rd fastest growing city in Canada". 10 February 2022.
- ^ "Langford leads growth in the province". Goldstreamgazette.com.
- ^ a b Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2021-10-27). "Census Profile, 2016 Census". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 2022-12-31.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2015-11-27). "NHS Profile". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 2022-12-31.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2019-08-20). "2006 Community Profiles". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 2022-12-31.
- ^ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2019-07-02). "2001 Community Profiles". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 2022-12-31.
- ^ "Millstream Village". Millstreamvillage.com.
- ^ "Westshore Town Centre – Welcome to Westshore Town Centre!". Westshoretowncentre.com.
- ^ "Cineplex.com – Cineplex Odeon Westshore". Cineplex.com.
- ^ "Cineplex Odeon to Open New Multiplex at Westshore Town Centre | Douglas magazine". Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "New cinema complex in Langford ready to open – BC Local News". Bclocalnews.com.
- ^ "Welcome to City Centre Park". Citycentrepark.ca. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "City of Langford – Family Fun Park". Cityoflangford.ca.
- ^ "City of Langford – Veterans Memorial Park". Cityoflangford.ca. Archived from the original on 2015-06-02. Retrieved 2015-05-17.
- ^ "Goldstream Station Market". Goldstreamstationmarket.ca.
- ^ "Luxton Fall Fair". Luxtonfair.ca.
- ^ "Rugby Canada". Rugbycanada.ca.
- ^ "Westhills – YMCA/YWCA – Langford Aquatic Centre". Durwest.com.
- ^ "City of Langford – YMCA/YWCA". Cityoflangford.ca. Archived from the original on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2015-05-17.
- ^ "The Westin Bear Mountain Golf Resort & Spa, Victoria". Bearmountain.ca.
- ^ "Mountain Biking at Bear Mountain Resort". Bearmountain.ca. Archived from the original on 2016-03-12. Retrieved 2015-05-17.
- ^ "South Island Disc Golf Society". Sidgs.org.
- ^ "South Island Intro". Naturehouse.ca.
- ^ "Goldstream Provincial Park, Salmon Run". Goldstreampark.com.
- ^ "City of Langford – Fire Department". Cityoflangford.ca.
- ^ "West Shore RCMP – About West Shore RCMP". Westshore.rcmp-grc.gc.ca. 26 May 2016.
- ^ "Westhills community in Langford expands its offerings". Vancouversun.com. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "'Boiling point': Malahat traffic angers commuters | CTV News". Vancouverisland.ctvnews.ca. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "Bear Mountain Resort developing next neighbourhood near Victoria". Biv.com. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "Alpine Group – Victoria BC". Alpinegroup.com.
- ^ "Our District | Sooke School District". 2023-12-13. Archived from the original on 2023-12-13. Retrieved 2023-12-13.
- ^ a b "New Schools – SD62 – School District #62 (Sooke)". Newschools.sd62.bc.ca.
- ^ "Lighthouse Christian Academy – Christian Education in Victoria BC". Lighthousechristianacademy.com.
- ^ McLeod, Andrew (2014-05-15). "Who is John Horgan?". The Tyee. Retrieved 2019-06-26.
External links
[edit]- Official website

 Langford travel guide from Wikivoyage
Langford travel guide from Wikivoyage