First-past-the-post voting
This article has an unclear citation style. (July 2024) |
It has been suggested that this article should be split into a new article titled Single-member district. (discuss) (September 2024) |
| A joint Politics and Economics series |
| Social choice and electoral systems |
|---|
 |
|
|
First-preference plurality (FPP)—often shortened simply to plurality—is a single-winner voting rule. Voters typically mark one candidate as their favorite, and the candidate with the largest number of first-preference marks (a plurality) is elected, regardless of whether they have over half of all votes (a majority). It is sometimes called first-past-the-post (FPTP) in reference to gambling on horse races (where bettors would guess which horse they thought would be first past the finishing post).[1][2][3] In social choice, FPP is generally treated as a degenerate variant of ranked voting, where voters rank the candidates, but only the first preference matters. As a result, FPP is usually implemented with a choose-one ballot, where voters place a single bubble next to their favorite candidate.
FPP has been used to elect the British House of Commons since the Middle Ages.[4] Throughout the 20th century, many countries that previously used FPP have abandoned it in favor of other electoral systems, including the former British colonies of Australia and New Zealand.
Most U.S. states still officially retain FPP for most elections. However, the combination of partisan primaries with the two-party system mean the country has effectively used a variation on the two-round system since the 1970s, where the first round selects two major contenders who go on to receive the overwhelming majority of votes.[5][6][7]

Example
[edit]
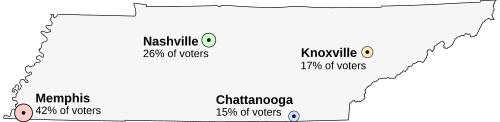
Suppose that Tennessee is holding an election on the location of its capital. The population is concentrated around four major cities. All voters want the capital to be as close to them as possible. The options are:
- Memphis, the largest city, but far from the others (42% of voters)
- Nashville, near the center of the state (26% of voters)
- Chattanooga, somewhat east (15% of voters)
- Knoxville, far to the northeast (17% of voters)
The preferences of each region's voters are:
| 42% of voters Far-West |
26% of voters Center |
15% of voters Center-East |
17% of voters Far-East |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
In FPTP, only the first preferences matter. As such, the votes would be counted as 42% for Memphis, 26% for Nashville, 17% for Knoxville, and 15% for Chattanooga. Since Memphis has the most votes, it would win a FPTP election, even though it is far from the center of the state and a majority of voters would prefer Nashville. Similarly, instant-runoff voting would elect Knoxville, the easternmost city. This makes the election a center squeeze. By contrast, both Condorcet methods and score voting would return Nashville (the capital of Tennessee).
Properties and effects
[edit]| Pathology | Explanation/details | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frustrated majority | The frustrated majority paradox occurs when a majority of voters prefer some candidate Alice to every other candidate, but Alice still loses the election. First-past-the-post is vulnerable to this paradox because of vote-splitting.[8] | |||
| Condorcet loser paradox | The Condorcet loser paradox happens when a majority of voters prefer every other candidate to A, but Alice still wins. First-past-the-post is vulnerable to this paradox because of vote-splitting.[8] | |||
| Center squeeze | The center-squeeze pathology occurs when a candidate who supports
| |||
| Spoiler effect | A spoiler effect is when the results of an election between A and B is affected by voters' opinions on an unrelated candidate C. First-past-the-post does not meet this criterion, which makes it vulnerable to spoilers. | |||
| Cloning paradox | The cloning paradox is a particular kind of spoiler effect that involves several perfect copies, or "clones", of a candidate. Candidate-cloning causes vote-splitting in FPP. | |||
| Best-is-worst paradox | The best-is-worst paradox occurs when an electoral system declares the same candidate to be in first and last place, depending on whether voters rank candidates from best-to-worst or worst-to-best. FPP demonstrates this pathology, because a candidate can be both the FPP winner and also the anti-plurality loser. | |||
| Lesser-evil voting | Lesser-evil voting occurs when voters are forced to support a "lesser of two evils" by rating them higher than their actual favorite candidate. FPP is vulnerable to this pathology. | |||
| Later-no-harm | Since plurality does not consider later preferences on the ballot at all, it is impossible to either harm or help a favorite candidate by marking later preferences. Thus it passes both Later-No-Harm and Later-No-Help. | |||
| Later-no-help | ||||
| Multiple-districts paradox | The multiple-districts paradox refers to a particularly egregious kind of gerrymander, when it is possible to draw a map where a candidate who loses the election nevertheless manages to win in every electoral district. This is not possible under FPP, or other positional voting methods. | |||
| Perverse response | Perverse response occurs when a candidate loses as a result of receiving too much support from some voters, i.e. it is possible for a candidate to lose by receiving too many votes. FPP is not affected by this pathology. | |||
| No-show paradox | The no-show paradox is a situation where a candidate loses as a result of having too many supporters. In other words, adding a voter who supports A over B can cause A to lose to B. FPP is not affected by this pathology. |
Two-party rule
[edit]
Perhaps the most striking effect of FPP is the fact that the number of a party's seats in a legislature has nothing to do with its vote count in an election, only in how those votes were geographically distributed. This has been a target of criticism for the method, many arguing that a fundamental requirement of an election system is to accurately represent the views of voters. FPP often creates "false majorities" by over-representing larger parties (giving a majority of the parliamentary/legislative seats to a party that did not receive a majority of the votes) while under-representing smaller ones. In Canada, majority governments have been formed due to one party winning a majority of the votes cast in Canada only three times since 1921: in 1940, 1958 and 1984. In the United Kingdom, 19 of the 24 general elections since 1922 have produced a single-party majority government. In all but two of them (1931 and 1935), the leading party did not take a majority of the votes across the UK.
In some cases, this can lead to a party receiving the plurality or even majority of total votes yet still failing to gain a plurality of legislative seats. This results in a situation called a majority reversal or electoral inversion.[9][10] Famous examples of the second-place party (in votes nationally) winning a majority of seats include the elections in Ghana in 2012, New Zealand in 1978 and 1981, and the United Kingdom in 1951. Famous examples of the second placed party (in votes nationally) winning a plurality of seats include the elections in Canada in 2019 and 2021 as well as in Japan in 2003. Even when a party wins more than half the votes in an almost purely two-party-competition, it is possible for the runner-up to win a majority of seats. This happened in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines in 1966, 1998, and 2020 and in Belize in 1993. Even with only two parties and equally-sized constituencies, winning a majority of seats just requires receiving more than half the vote in more than half the districts—even if the other party receives all the votes cast in the other districts—so just over a quarter of the vote is theoretically enough to win a majority in the legislature. With enough candidates splitting the vote in a district, the total number of votes needed to win can be made arbitrarily small.[citation needed]
Two-party systems
[edit]Under first-past-the-post, a small party may draw votes and seats away from a larger party that it is more similar to, and therefore give an advantage to one it is less similar to. For example, in the 2000 United States presidential election, the left-leaning Ralph Nader drew more votes from the left-leaning Al Gore, resulting in Nader spoiling the election for the Democrats. According to the political pressure group Make Votes Matter, FPTP creates a powerful electoral incentive for large parties to target similar segments of voters with similar policies. The effect of this reduces political diversity in a country because the larger parties are incentivized to coalesce around similar policies.[11] The ACE Electoral Knowledge Network describes India's use of FPTP as a "legacy of British colonialism".[12]
Duverger's law is an idea in political science which says that constituencies that use first-past-the-post methods will lead to two-party systems, given enough time. Economist Jeffrey Sachs explains:
The main reason for America's majoritarian character is the electoral system for Congress. Members of Congress are elected in single-member districts according to the "first-past-the-post" (FPTP) principle, meaning that the candidate with the plurality of votes is the winner of the congressional seat. The losing party or parties win no representation at all. The first-past-the-post election tends to produce a small number of major parties, perhaps just two, a principle known in political science as Duverger's Law. Smaller parties are trampled in first-past-the-post elections.
— from Sachs's The Price of Civilization, 2011[13]
However, most countries with first-past-the-post elections have multiparty legislatures (albeit with two parties larger than the others), the United States being the major exception.[14] There is a counter-argument to Duverger's Law, that while on the national level a plurality system may encourage two parties, in the individual constituencies supermajorities will lead to the vote fracturing.[15]
Strongholds, key constituencies and kingmakers
[edit]It has been suggested that the distortions in geographical representation provide incentives for parties to ignore the interests of areas in which they are too weak to stand much chance of gaining representation, leading to governments that do not govern in the national interest. Further, during election campaigns the campaigning activity of parties tends to focus on marginal seats where there is a prospect of a change in representation, leaving safer areas excluded from participation in an active campaign.[16] Political parties operate by targeting districts, directing their activists and policy proposals toward those areas considered to be marginal, where each additional vote has more value.[17][18][19]
This feature of FPTP has often been used by its supporters in contrast to proportional systems. In the latter, smaller parties act as 'kingmakers' in coalitions as they have greater bargaining power and therefore, arguably, their influence on policy is disproportional to their parliamentary size- this is largely avoided in FPP systems where majorities are generally achieved.[20] FPP often produces governments which have legislative voting majorities,[21] thus providing such governments the legislative power necessary to implement their electoral manifesto commitments during their term in office. This may be beneficial for the country in question in circumstances where the government's legislative agenda has broad public support, albeit potentially divided across party lines, or at least benefits society as a whole. However handing a legislative voting majority to a government which lacks popular support can be problematic where said government's policies favor only that fraction of the electorate that supported it, particularly if the electorate divides on tribal, religious, or urban–rural lines. There is also the perceived issue of unfair coalitions where a smaller party can form a coalition with other smaller parties and form a government, without a clear mandate as was the case in the 2009 Israeli legislative election where the leading party Kadima, was unable to form a coalition so Likud, a smaller party, managed to form a government without being the largest party. The use of proportional representation (PR) may enable smaller parties to become decisive in the country's legislature and gain leverage they would not otherwise enjoy, although this can be somewhat mitigated by a large enough electoral threshold. They argue that FPP generally reduces this possibility, except where parties have a strong regional basis. A journalist at Haaretz noted that Israel's highly proportional Knesset "affords great power to relatively small parties, forcing the government to give in to political blackmail and to reach compromises";[22][23] Tony Blair, defending FPP, argued that other systems give small parties the balance of power, and influence disproportionate to their votes.[24]
The concept of kingmakers is adjacent to how Winston Churchill criticized the alternative vote system as "determined by the most worthless votes given for the most worthless candidates."[25] meaning that votes for the least supported candidates may change the outcome of the election between the most supported candidates. In this case however, this is a feature of the alternative vote, since those votes would have otherwise been wasted (and in some sense this makes every vote count, as opposed to FPP), and this effect is only possible when no candidate receives an outright majority of first preference votes. it is related to kingmakers in that the lesser-known candidates may encourage their supporters to rank the other candidates a certain way. Supporters of electoral reform generally see this as a positive development, and claim that alternatives certain to FPP will encourage less negative and more positive campaigning, as candidates will have to appeal to a wider group of people. Opinions are split on whether the alternative vote (better known as instant runoff voting outside the UK) achieves this better than other systems.
Extremist parties
[edit]Supporters and opponents of FPP often argue whether FPP advantages or disadvantages extremist parties. Among single-winner systems, FPP suffers from the center squeeze phenomenon, where more moderate candidates are squeezed out by more extreme ones. However, the different types (or the absence of) of party primaries maybe strengthen or weaken this effect. In general, FPP has no mechanism that would benefit more moderate candidates and many supporters of FPP defend it electing the largest and most unified (even if more polarizing) minority over a more consensual majority supported candidate. Allowing people into parliament who did not finish first in their district was described by David Cameron as creating a "Parliament full of second-choices who no one really wanted but didn't really object to either."[26]
However, FPP often results in strategic voting, which has prevented extreme left- and right-wing parties from gaining parliamentary seats[citation needed], as opposed to proportional representation. This also implies that strategic voting is necessary to keep extremists from gaining seats, which often fails to materialize in practice for multiple reasons. In comparison, many other systems encourage voters to rank other candidates and thereby not (or at least less often to) have to strategically compromise on their first choice at the same time.
On the other hand, the Constitution Society published a report in April 2019 stating that, "[in certain circumstances] FPP can ... abet extreme politics, since should a radical faction gain control of one of the major political parties, FPP works to preserve that party's position. ...This is because the psychological effect of the plurality system disincentivises a major party's supporters from voting for a minor party in protest at its policies, since to do so would likely only help the major party's main rival. Rather than curtailing extreme voices, FPP today empowers the (relatively) extreme voices of the Labour and Conservative party memberships."[27][28] For example, the electoral system of Hungary, a mixed system dominated by FPP have seen Fidesz (right-wing, populist party) win 135 seats in the 2022 Hungarian parliamentary election and has remained the largest party in Hungary since 2010 by changing the electoral system to mostly use FPP instead of the previous mixed system using mostly the two-round system. Since 2010, Fidesz has implemented other anti-democratic reforms that now mean the European Parliament no longer qualifies Hungary as a full democracy.[29] Electoral reform campaigners have argued that the use of FPP in South Africa was a contributory factor in the country adopting the apartheid system after the 1948 general election in that country.[30][31] Leblang and Chan found that a country's electoral system is the most important predictor of a country's involvement in war, according to three different measures: (1) when a country was the first to enter a war; (2) when it joined a multinational coalition in an ongoing war; and (3) how long it stayed in a war after becoming a party to it.[32][33] When the people are fairly represented in parliament, more of those groups who may object to any potential war have access to the political power necessary to prevent it. In a proportional democracy, war and other major decisions generally requires the consent of the majority.[33][34][35] The British human rights campaigner Peter Tatchell, and others, have argued that Britain entered the Iraq War primarily because of the political effects of FPP and that proportional representation would have prevented Britain's involvement in the war.[36][37][38]
Tactical voting
[edit]To a greater extent than many others, the first-past-the-post method encourages "tactical voting". Voters have an incentive to vote for a candidate who they predict is more likely to win, as opposed to their preferred candidate who may be unlikely to win and for whom a vote could be considered as wasted. FPP wastes fewer votes when it is used in two-party contests. But waste of votes and minority governments are more likely when large groups of voters vote for three, four or more parties as in Canadian elections. Canada uses FPP and only two of the last seven federal Canadian elections (2011 and 2015) produced single-party majority governments. In none of them did the leading party receive a majority of the votes.
The position is sometimes summarized, in an extreme form, as "all votes for anyone other than the runner-up are votes for the winner."[39] This is because votes for these other candidates deny potential support from the second-placed candidate, who might otherwise have won. Following the extremely close 2000 U.S. presidential election, some supporters of Democratic candidate Al Gore believed one reason he lost to Republican George W. Bush is that a portion of the electorate (2.7%) voted for Ralph Nader of the Green Party, and exit polls indicated that more of them would have preferred Gore (45%) to Bush (27%).[40] The election was ultimately determined by the results from Florida, where Bush prevailed over Gore by a margin of only 537 votes (0.009%), which was far exceeded by the 97488 (1.635%) votes cast for Nader in that state.
In Puerto Rico, there has been a tendency for Independentista voters to support Populares candidates. This phenomenon is responsible for some Popular victories, even though the Estadistas have the most voters on the island, and is so widely recognised that Puerto Ricans sometimes call the Independentistas who vote for the Populares "melons", because that fruit is green on the outside but red on the inside (in reference to the party colors).
Because voters have to predict who the top two candidates will be, results can be significantly distorted:
- Some voters will vote based on their view of how others will vote as well, changing their originally intended vote;
- Substantial power is given to the media, because some voters will believe its assertions as to who the leading contenders are likely to be. Even voters who distrust the media will know that others do believe the media, and therefore those candidates who receive the most media attention will probably be the most popular;
- A new candidate with no track record, who might otherwise be supported by the majority of voters, may be considered unlikely to be one of the top two, and thus lose votes to tactical voting;
- The method may promote votes against as opposed to votes for. For example, in the UK (and only in the Great Britain region), entire campaigns have been organised with the aim of voting against the Conservative Party by voting Labour, Liberal Democrat in England and Wales, and since 2015 the SNP in Scotland, depending on which is seen as best placed to win in each locality. Such behavior is difficult to measure objectively.
Proponents of other voting methods in single-member districts argue that these would reduce the need for tactical voting and reduce the spoiler effect. Examples include preferential voting systems, such as instant runoff voting, as well as the two-round system of runoffs and less tested methods such as approval voting and Condorcet methods. Wasted votes are seen as those cast for losing candidates, and for winning candidates in excess of the number required for victory. For example, in the UK general election of 2005, 52% of votes were cast for losing candidates and 18% were excess votes—a total of 70% "wasted" votes. On this basis a large majority of votes may play no part in determining the outcome. This winner-takes-all system may be one of the reasons why "voter participation tends to be lower in countries with FPP than elsewhere."[41]
Geography
[edit]The effect of a system based on plurality voting spread over many separate districts is that the larger parties, and parties with more geographically concentrated support, gain a disproportionately large share of seats, while smaller parties with more evenly distributed support gain a disproportionately small share. This is because in doing this they win many seats and do not 'waste' many votes in other areas. As voting patterns are similar in about two-thirds of the districts, it is more likely that a single party will hold a majority of legislative seats under FPP than happens in a proportional system, and under FPP it is rare to elect a majority government that actually has the support of a majority of voters. Because FPP permits many wasted votes, an election under FPP is more easily gerrymandered. Through gerrymandering, electoral areas are designed deliberately to unfairly increase the number of seats won by one party by redrawing the map such that one party has a small number of districts in which it has an overwhelming majority of votes (whether due to policy, demographics which tend to favor one party, or other reasons), and many districts where it is at a smaller disadvantage.[citation needed]
The British Electoral Reform Society (ERS) says that regional parties benefit from this system. "With a geographical base, parties that are small UK-wide can still do very well".[42]
On the other hand, minor parties that do not concentrate their vote usually end up getting a much lower proportion of seats than votes, as they lose most of the seats they contest and 'waste' most of their votes.[19]
The ERS also says that in FPP elections using many separate districts "small parties without a geographical base find it hard to win seats".[42]
Make Votes Matter said that in the 2017 general election, "the Green Party, Liberal Democrats and UKIP (minor, non-regional parties) received 11% of votes between them, yet they shared just 2% of seats", and in the 2015 general election, "[t]he same three parties received almost a quarter of all the votes cast, yet these parties shared just 1.5% of seats."[43]
According to Make Votes Matter, in the 2015 UK general election UKIP came in third in terms of number of votes (3.9 million/12.6%), but gained only one seat in Parliament, resulting in one seat per 3.9 million votes. The Conservatives on the other hand received one seat per 34,000 votes.[43]
The winner-takes-all nature of FPP leads to distorted patterns of representation, since it exaggerates the correlation between party support and geography.
For example, in the UK the Conservative Party represents most of the rural seats in England, and most of the south of England, while the Labour Party represents most of the English cities and most of the north of England.[44] This pattern hides the large number of votes for the non-dominant party. Parties can find themselves without elected politicians in significant parts of the country, heightening feelings of regionalism. Party supporters (who may nevertheless be a significant minority) in those sections of the country are unrepresented.
In the 2019 Canadian federal election Conservatives won 98% of the seats in Alberta and Saskatchewan with only 68% of the vote. The lack of non-Conservative representation gives the appearance of greater Conservative support than actually exists.[45] Similarly, in Canada's 2021 elections, the Conservative Party won 88% of the seats in Alberta with only 55% of the vote, and won 100% of the seats in Saskatchewan with only 59% of the vote.[46]
First-past-the-post within geographical areas tends to deliver (particularly to larger parties) a significant number of safe seats, where a representative is sheltered from any but the most dramatic change in voting behavior. In the UK, the Electoral Reform Society estimates that more than half the seats can be considered as safe.[47] It has been claimed that members involved in the 2009 expenses scandal were significantly more likely to hold a safe seat.[48][49]
History
[edit]The House of Commons of England originated in the Middle Ages as an assembly representing the gentry of the counties and cities of the Kingdom, each of which elected either one or two members of parliament (MPs) by block plurality voting. Starting in the 19th century, electoral reform advocates pushed to replace these multi-member constituencies with single-member districts.[citation needed] Elections to the Canadian House of Commons have always been conducted with FPP.[citation needed]
The United States broke away from British rule in the late 18th century, and its constitution provides for an electoral college to elect its president. Despite original intentions to the contrary, by the mid-19th century this college had transformed into a de facto use of FPP for each state's presidential election. This further morphed through the introduction of the party primary, which made American elections into a two-round system in practice.
Criticism and replacement
[edit]Non-plurality voting systems have been devised since at least 1299, when Ramon Llull came up with both the Condorcet and Borda count methods, which were respectively reinvented in the 18th century by the Marquis de Condorcet and Jean-Charles de Borda. More serious investigation into electoral systems came in the late 18th century, when several thinkers independently proposed systems of proportional representation to elect legislatures. The single transferable vote in particular was invented in 1819 by Thomas Wright Hill, and first used in a public election in 1840 by his son Rowland for the Adelaide City Council in Australia. STV saw its first national use in Denmark in 1855, and was reinvented several times in the 19th century.
The Proportional Representation Society was founded in England in 1884 and began campaigning. STV was used to elect the British House of Commons's university constituencies between 1918 and their abolition in 1950.[citation needed]
Many countries which use FPP have active campaigns to switch to proportional representation (e.g. UK[50] and Canada[51]). Most modern democracies use some form of proportional representation.[52][53]
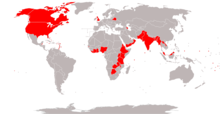
Countries using FPP
[edit]Legislatures elected exclusively by single-member plurality
[edit]The following is a list of countries currently following the first-past-the-post voting system for their national legislatures.[54][55]

 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bahamas
Bahamas Bangladesh
Bangladesh Barbados
Barbados Belarus
Belarus Belize
Belize Botswana
Botswana Canada (for the lower house only)
Canada (for the lower house only) Dominica
Dominica Eritrea
Eritrea Eswatini
Eswatini Ethiopia
Ethiopia The Gambia
The Gambia Ghana
Ghana Grenada
Grenada India (for the lower house only)
India (for the lower house only) Jamaica
Jamaica Kenya
Kenya Liberia
Liberia Malaysia
Malaysia Malawi
Malawi Maldives
Maldives Mauritius
Mauritius Federated States of Micronesia
Federated States of Micronesia Myanmar (both houses)
Myanmar (both houses) Nigeria (both houses)
Nigeria (both houses) Palau (lower house only)
Palau (lower house only) Qatar
Qatar Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa
Samoa Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Tonga
Tonga Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago Uganda
Uganda United Kingdom (for the lower house only)
United Kingdom (for the lower house only) Yemen
Yemen Zambia
Zambia
Upper house only
[edit]Varies by state
[edit] United States (both houses)[footnote 1]
United States (both houses)[footnote 1]
Subnational legislatures
[edit] Cook Islands (New Zealand)
Cook Islands (New Zealand) US Virgin Islands
US Virgin Islands Bermuda
Bermuda Cayman Islands
Cayman Islands
Use of single-member plurality in mixed systems for electing legislatures
[edit]The following countries use single-member plurality to elect part of their national legislature, in different types of mixed systems.
Alongside block voting (fully majoritarian systems) or as part of mixed-member majoritarian systems (semi-proportional representation)
 Brazil – in the Federal Senate, alongside plurality block voting (alternating elections)
Brazil – in the Federal Senate, alongside plurality block voting (alternating elections) Hungary – as part is a mixed system (parallel voting with partial compensation)
Hungary – as part is a mixed system (parallel voting with partial compensation) Ivory Coast – in single-member electoral districts, alongside party block voting
Ivory Coast – in single-member electoral districts, alongside party block voting Iran – in single-member electoral districts for Khobregan, alongside plurality block voting
Iran – in single-member electoral districts for Khobregan, alongside plurality block voting Marshall Islands – in single-member electoral districts, alongside plurality block voting
Marshall Islands – in single-member electoral districts, alongside plurality block voting Oman – in single-member electoral districts, alongside plurality block voting
Oman – in single-member electoral districts, alongside plurality block voting Pakistan – alongside seats distributed proportional to seats already won
Pakistan – alongside seats distributed proportional to seats already won Singapore – in single-member electoral districts, alongside party block voting
Singapore – in single-member electoral districts, alongside party block voting Republic of China (Taiwan) – as part is a mixed system (parallel voting)
Republic of China (Taiwan) – as part is a mixed system (parallel voting)
As part of mixed-member proportional (MMP) or additional member systems (AMS)
 Bolivia
Bolivia Lesotho
Lesotho New Zealand
New Zealand South Korea – as part is a mixed system (AMS and parallel voting)
South Korea – as part is a mixed system (AMS and parallel voting)
Subnational legislatures
 Scotland (United Kingdom)
Scotland (United Kingdom)
Heads of state elected by FPP
[edit] Angola (Double simultaneous vote for the presidential and legislative elections)
Angola (Double simultaneous vote for the presidential and legislative elections) Bosnia and Herzegovina (one for each main ethnic group)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (one for each main ethnic group) Cameroon
Cameroon Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea The Gambia
The Gambia Guyana (Double simultaneous vote for the presidential and legislative elections)
Guyana (Double simultaneous vote for the presidential and legislative elections) Honduras
Honduras Iceland
Iceland Kiribati
Kiribati Malawi
Malawi Mexico
Mexico Nicaragua
Nicaragua Nigeria
Nigeria Palestine
Palestine Panama
Panama Paraguay
Paraguay Philippines
Philippines Rwanda
Rwanda Singapore
Singapore South Korea
South Korea Taiwan (from 1996 constitutional amendment)
Taiwan (from 1996 constitutional amendment) Tanzania
Tanzania Venezuela
Venezuela
Former use
[edit]- Argentina (The Chamber of Deputies uses party list PR. Only twice used FPTP, first between 1902 and 1905 used only in the elections of 1904,[57] and the second time between 1951 and 1957 used only in the elections of 1951 and 1954.)[58]
- Australia (replaced by IRV in 1918 for both the House of Representatives and the Senate, with STV being introduced to the Senate in 1948)
- Belgium (adopted in 1831, replaced by party list PR in 1899)—[59] the Member of the European Parliament for the German-speaking electoral college is still elected by FPTP[60]
- Cyprus (replaced by proportional representation in 1981)
- Denmark (replaced by proportional representation in 1920)
- Hong Kong (adopted in 1995, replaced by party list PR in 1998)
- Italy (used between 1860 and 1882, and between 1892 and 1919)
- Japan (replaced by parallel voting in 1993)
- Lebanon (replaced by proportional representation in June 2017)
- Lesotho (replaced by MMP Party list in 2002)
- Malta (replaced by STV in 1921)
- Mexico (replaced by parallel voting in 1977)
- Nepal (replaced by parallel voting)[61]
- Netherlands (replaced by party list PR in 1917)[62]
- New Zealand (replaced by MMP in 1996)
- Papua New Guinea (replaced by IRV in 2002)[63]
- Philippines (replaced by parallel voting in 1998 for House of Representatives elections, and by multiple non-transferable vote in 1941 for Senate elections)
- Portugal (replaced by party list PR)[64]
- Serbia (adopted in 1990, replaced by party list PR in 1992)[65]
- South Africa (replaced by party list PR in 1994)
- Tanzania (replaced by parallel voting in 1995)
See also
[edit]- Cube rule
- Deviation from proportionality
- Plurality-at-large voting
- Approval voting
- Single non-transferable vote
- Single transferable vote
References
[edit]- ^ "First-past-the-post: a rogue's practice?". On Elections. 31 July 2018. Retrieved 9 September 2024.
- ^ "First past the post". nzhistory.govt.nz. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 13 January 2016. Archived from the original on 24 May 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ^ "First Past the Post and Alternative Vote explained". gov.uk. 6 September 2010. Archived from the original on 18 January 2024. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
- ^ "The Boundaries Review is a chance to bring back multi-member constituencies". 26 September 2016.
- ^ Santucci, Jack; Shugart, Matthew; Latner, Michael S. (16 October 2023). "Toward a Different Kind of Party Government". Protect Democracy. Archived from the original on 16 July 2024. Retrieved 16 July 2024.
Finally, we should not discount the role of primaries. When we look at the range of countries with first-past-the-post (FPTP) elections (given no primaries), none with an assembly larger than Jamaica's (63) has a strict two-party system. These countries include the United Kingdom and Canada (where multiparty competition is in fact nationwide). Whether the U.S. should be called 'FPTP' itself is dubious, and not only because some states (e.g. Georgia) hold runoffs or use the alternative vote (e.g. Maine). Rather, the U.S. has an unusual two-round system in which the first round winnows the field. This usually is at the intraparty level, although sometimes it is without regard to party (e.g. in Alaska and California).
- ^ Gallagher, Michael; Mitchell, Paul (15 September 2005). "The American Electoral System". The Politics of Electoral Systems. OUP Oxford. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-19-153151-4.
American elections become a two-round run-off system with a delay of several months between the rounds.
- ^ Bowler, Shaun; Grofman, Bernard; Blais, André (2009), "The United States: A Case of Duvergerian Equilibrium", Duverger's Law of Plurality Voting: The Logic of Party Competition in Canada, India, the United Kingdom and the United States, New York, NY: Springer, pp. 135–146, doi:10.1007/978-0-387-09720-6_9, ISBN 978-0-387-09720-6, retrieved 31 August 2024,
In effect, the primary system means that the USA has a two-round runoff system of elections.
- ^ a b Felsenthal, Dan S. (2010) Review of paradoxes afflicting various voting procedures where one out of m candidates (m ≥ 2) must be elected Archived 24 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine. In: Assessing Alternative Voting Procedures, London School of Economics and Political Science, London, UK.
- ^ Geruso, Michael; Spears, Dean; Talesara, Ishaana (5 September 2019). "Inversions in US Presidential Elections: 1836-2016". American Economic Journal: Applied Economics. 14 (1): 327–357. doi:10.3386/w26247. PMC 10782436. PMID 38213750. Archived from the original on 19 March 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ Miller, Nicholas R. "Election Inversions By Variants of the U.S. Electoral College". Department of Political Science. UMBC. Archived from the original on 18 July 2021. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
- ^ "First Past the Post". Make Votes Matter. Archived from the original on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ "India – First Past the Post on a Grand Scale". ACE Electoral Knowledge Network. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- ^ Sachs, Jeffrey (2011). The Price of Civilization. New York: Random House. p. 107. ISBN 978-1-4000-6841-8.
- ^ Dunleavy, Patrick; Diwakar, Rekha (2013). "Analysing multiparty competition in plurality rule elections" (PDF). Party Politics. 19 (6): 855–886. doi:10.1177/1354068811411026. S2CID 18840573. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 June 2022. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- ^ Dickson, Eric S.; Scheve, Kenneth (2010). "Social Identity, Electoral Institutions and the Number of Candidates". British Journal of Political Science. 40 (2): 349–375. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.75.155. doi:10.1017/s0007123409990354. JSTOR 40649446. S2CID 7107526.
- ^ "First Past the Post is a 'broken voting system'". ippr.org. Institute for Public Policy Research. 4 January 2011. Archived from the original on 15 November 2017. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ Terry, Chris (28 August 2013). "In Britain's first past the post electoral system, some votes are worth 22 times more than others". democraticaudit.com. London School of Economics. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ Galvin, Ray. "What is a marginal seat?". justsolutions.eu. Archived from the original on 15 November 2017. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ a b "First Past the Post". electoral-reform.org.uk. Archived from the original on 13 December 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- ^ Brams/Kilgour. Dorey (2013). "Kingmakers and leaders in coalition formation". Social Choice and Welfare. 41 (1): 1–18. doi:10.1007/s00355-012-0680-4. hdl:10419/53209. JSTOR 42001390. S2CID 253849669. Archived from the original on 11 March 2023. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ Andy Williams (1998). UK Government & Politics. Heinemann. p. 24. ISBN 978-0-435-33158-0. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 11 October 2016.
- ^ Ilan, Shahar. "Major Reforms Are Unlikely, but Electoral Threshold Could Be Raised". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 21 August 2019. Retrieved 8 May 2010.
- ^ Dr.Mihaela Macavei, University of Alba Iulia, Romania. "Advantages and disadvantages of the uninominal voting system" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2019. Retrieved 8 May 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ P. Dorey (17 June 2008). The Labour Party and Constitutional Reform: A History of Constitutional Conservatism. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 400–. ISBN 978-0-230-59415-9.
- ^ Larry Johnston (13 December 2011). Politics: An Introduction to the Modern Democratic State. University of Toronto Press. pp. 231–. ISBN 978-1-4426-0533-6.
- ^ "David Cameron. "David Cameron: why keeping first past the post is vital for democracy Archived 18 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine." Daily Telegraph. 30 April 2011
- ^ Walker, Peter (22 April 2019). "First past the post abets extreme politics, says thinktank". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 6 December 2023. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ "The Electoral System and British Politics". consoc.org.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2020. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ "MEPs: Hungary can no longer be considered a full democracy" (Press release). European Parliament. 15 September 2022. Archived from the original on 15 September 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2023.
- ^ Cowen, Doug. "The Graveyard of First Past the Post". Electoral Reform Society. Archived from the original on 4 July 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- ^ Winter, Owen (25 August 2016). "How a Broken Voting System Gave South Africa Apartheid in 1948". Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 18 March 2021. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- ^ Leblang, D.; Chan, S. (2003). "Explaining Wars Fought By Established Democracies: Do Institutional Constraints Matter?". Political Research Quarterly: 56-24: 385–400.
- ^ a b "PR and Conflict". Make Votes Matter. Archived from the original on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ "What the Evidence Says". Fair Voting BC. 19 November 2017. Archived from the original on 29 June 2020. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ "Democracy: we've never had it so bad". The Guardian. 3 May 2010. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ^ Tatchell, Peter (3 May 2010). "Democracy: we've never had it so bad". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ Barnett, Anthony (10 January 2020). "Will Labour's next leader finally break with first-past-the-post?". Labourlist.org. Archived from the original on 5 July 2020. Retrieved 5 July 2020.
- ^ Root, Tim (30 September 2019). "Making government accountable to the people". Left Foot Forward. Archived from the original on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 5 July 2020.
- ^ Begany, Brent (30 June 2016). "The 2016 Election Proves The Need For Voting Reform". Policy Interns. Archived from the original on 22 October 2019. Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- ^ Rosenbaum, David E. (24 February 2004). "THE 2004 CAMPAIGN: THE INDEPENDENT; Relax, Nader Advises Alarmed Democrats, but the 2000 Math Counsels Otherwise". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 19 September 2008. Retrieved 7 February 2017.
- ^ Drogus, Carol Ann (2008). Introducing comparative politics: concepts and cases in context. CQ Press. pp. 257. ISBN 978-0-87289-343-6.
- ^ a b "First Past the Post". electoral-reform.org.uk. Archived from the original on 13 December 2019. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- ^ a b "Make Votes Matter—Everything wrong with First Past the Post—Proportional Representation". Make Votes Matter. Archived from the original on 2 November 2019. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- ^ Beech, Matt; Hickson, Kevin (3 July 2020). "Divided by Values: Jeremy Corbyn, the Labour Party and England's 'North-South Divide'". Revue Française de Civilisation Britannique. XXV (2). doi:10.4000/rfcb.5456. S2CID 198655613.
- ^ "First Past the Post". conservativeelectoralreform.org. Conservative Action for Electoral Reform. Archived from the original on 15 November 2017. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ "Elections Canada – Results by Province(s)". 2021 Elections Canada – Provinces. Elections Canada. 21 September 2020. Archived from the original on 9 December 2022. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ "General Election 2010: Safe and marginal seats". The Guardian. 7 April 2010. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ Wickham, Alex. ""Safe seats" almost guarantee corruption". thecommentator.com. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ "FactCheck: expenses and safe seats". channel4.com. Channel 4. Archived from the original on 8 May 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2017.
- ^ "What We Stand For". electoral-reform.org.uk. Archived from the original on 26 June 2020. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- ^ "Home". Fair Vote Canada. Archived from the original on 1 July 2020. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- ^ "Electoral Systems around the World". FairVote.org. Archived from the original on 11 September 2021. Retrieved 18 July 2020.
- ^ "Labour Campaign for Electoral Reform – About LCER". labourcampaignforelectoralreform.org.uk. Archived from the original on 11 August 2021. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
- ^ "Countries using FPTP electoral system for national legislature". idea.int. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 3 December 2018.
- ^ "Electoral Systems". ACE Electoral Knowledge Network. Archived from the original on 26 August 2014. Retrieved 3 November 2015.
- ^ "Electoral College Frequently Asked Questions". National Archives. 6 July 2023. Archived from the original on 6 December 2023. Retrieved 23 October 2015.
- ^ Milia, Juan Guillermo (2015). El Voto. Expresión del poder ciudadano. Buenos Aires: Editorial Dunken. pp. 40–41. ISBN 978-987-02-8472-7.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Law 14,032". Sistema Argentino de Información Jurídica. Archived from the original on 20 October 2017. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
- ^ "Kiesstelsel. §1.1 Federale verkiezingen". Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins. Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. 1993–2002.
- ^ "Elections 2019: The European Parliament". Flanders News. 17 April 2019. Archived from the original on 6 April 2023. Retrieved 2 December 2022.
The European Parliament elections in Belgium will be held on 26 May, the same day as the regional and federal elections. In the European elections there are three Belgian constituencies: the Dutch-speaking electoral college, the Francophone electoral college and the German-speaking electoral college.
- ^ Bhuwan Chandra Upreti (2010). Nepal: Transition to Democratic Republican State : 2008 Constituent Assembly. Gyan Publishing House. pp. 69–. ISBN 978-81-7835-774-4. Archived from the original on 22 May 2024. Retrieved 11 October 2016.
- ^ Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "Kiesstelsel. §1.1 Geschiedenis". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum.
- ^ "PNG voting system praised by new MP". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 12 December 2003. Archived from the original on 4 January 2005. Retrieved 19 May 2015.
- ^ "Which European countries use proportional representation?". electoral-reform.org.uk. Archived from the original on 27 December 2019. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- ^ MrdaljPolitikolog, Mladen; Univerzitetu, Predavač na Webster (8 October 2020). "Sedam zabluda o uvođenju većinskog izbornog sistema". Talas.rs. Archived from the original on 13 January 2024. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
- ^ Prior to the 2020 election, the US states of Alaska and Maine completely abandoned FPTP in favor of Instant-runoff voting or IRV. In the US, 48 of the 50 states and the District of Columbia use FPTP-GT to choose the electors of the Electoral College (which in turn elects the president); Maine and Nebraska use a variation where the electoral vote of each congressional district is awarded by FPTP (or by IRV in Maine beginning in 2020), and the statewide winner (using the same method used in each congressional district in the state) is awarded an additional two electoral votes. In states that employ FPTP-GT, the presidential candidate gaining the greatest number of votes wins all the state's available electors (seats), regardless of the number or share of votes won (majority vs non-majority plurality), or the difference separating the leading candidate and the first runner-up.[56]
External links
[edit]- A handbook of Electoral System Design from International IDEA
- ACE Project: What is the electoral system for Chamber 1 of the national legislature?
- ACE Project: First Past The Post—detailed explanation of first-past-the-post voting
- ACE Project: Electing a President using FPTP
- ACE Project: FPTP on a grand scale in India
- The Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform says the new proportional electoral system it proposes for British Columbia will improve the practice of democracy in the province.
- Vote No to Proportional Representation BC
- Fact Sheets on Electoral Systems provided to members of the Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform, British Columbia.
- The Problem With First-Past-The-Post Electing (data from UK general election 2005)
- The Problems with First Past the Post Voting Explained (video) on YouTube
- The fatal flaws of First-past-the-post electoral systems