Matrix representation
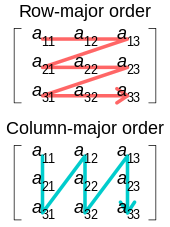
Matrix representation is a method used by a computer language to store column-vector matrices of more than one dimension in memory. Fortran and C use different schemes for their native arrays. Fortran uses "Column Major" (AoS), in which all the elements for a given column are stored contiguously in memory. C uses "Row Major" (SoA), which stores all the elements for a given row contiguously in memory. LAPACK defines various matrix representations in memory. There is also Sparse matrix representation and Morton-order matrix representation. According to the documentation, in LAPACK the unitary matrix representation is optimized.[1][2] Some languages such as Java store matrices using Iliffe vectors. These are particularly useful for storing irregular matrices. Matrices are of primary importance in linear algebra.
Basic mathematical operations
[edit]An m × n (read as m by n) order matrix is a set of numbers arranged in m rows and n columns. Matrices of the same order can be added by adding the corresponding elements. Two matrices can be multiplied, the condition being that the number of columns of the first matrix is equal to the number of rows of the second matrix. Hence, if an m × n matrix is multiplied with an n × r matrix, then the resultant matrix will be of the order m × r.[3]
Operations like row operations or column operations can be performed on a matrix, using which we can obtain the inverse of a matrix. The inverse may be obtained by determining the adjoint as well.[3] rows and columns are the different classes of matrices
In 3D graphics
[edit]The choice of representation for 4×4 matrices commonly used in 3D graphics affects the implementation of matrix/vector operations in systems with packed SIMD instructions:
Row major (SoA)
[edit]With row-major matrix order, it is easy to transform vectors using dot product operations, since the coefficients of each component are sequential in memory. Consequently, this layout may be desirable if a processor supports dot product operations natively. It is also possible to efficiently use a '3×4' affine transformation matrix without padding or awkward permutes.
Column major (AoS)
[edit]With column-major order, a "matrix × vector" multiply can be implemented with vectorized multiply-add operations, if the vector's components are broadcast to each SIMD lane. It is also easy to access the basis vectors represented by a transformation matrix as individual column vectors, as these are contiguous in memory.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Representation of Orthogonal or Unitary Matrices". University of Texas at Austin. Retrieved 14 September 2011.
- ^ Lehoucq, R. (1996). "The Computation of Elementary Unitary Matrices". ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software. 22 (4): 393–400. doi:10.1145/235815.235817. hdl:1911/101830.
- ^ a b Ramana, B.V (2008). Higher Engineering Mathematics. New Delhi: Tata Mcgraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-063419-0.
